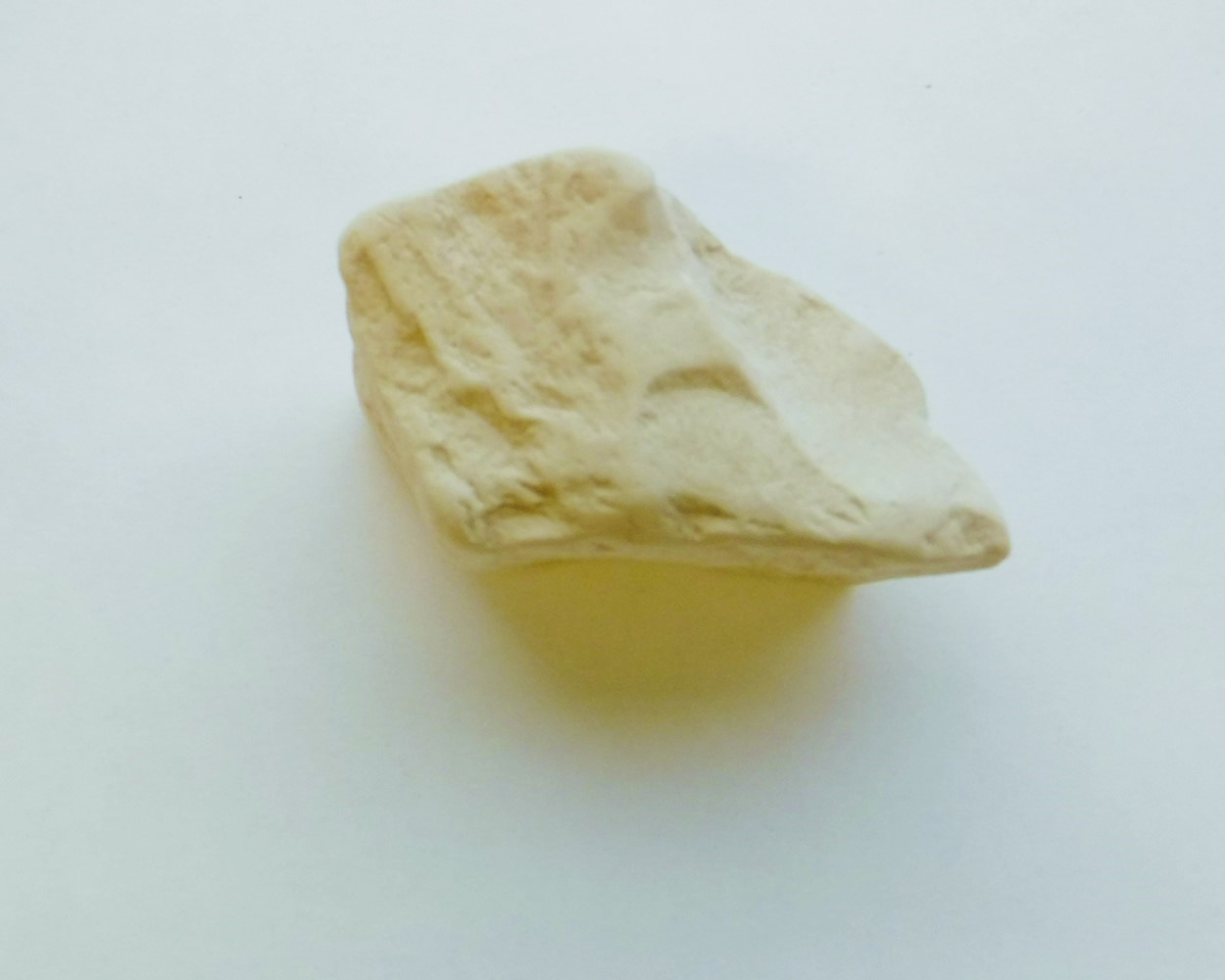
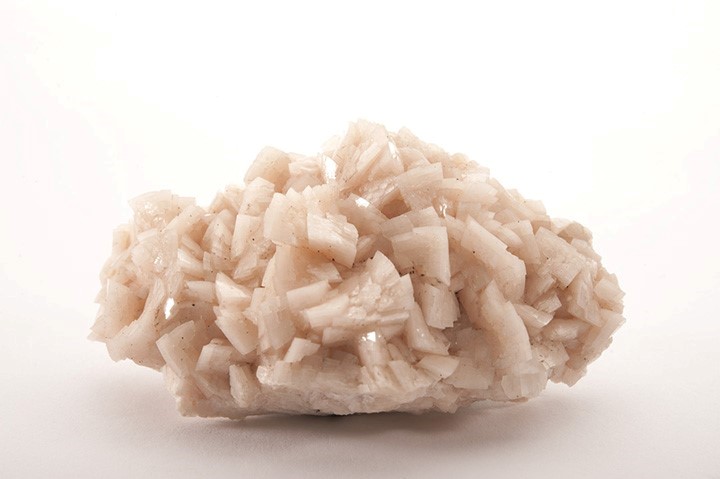
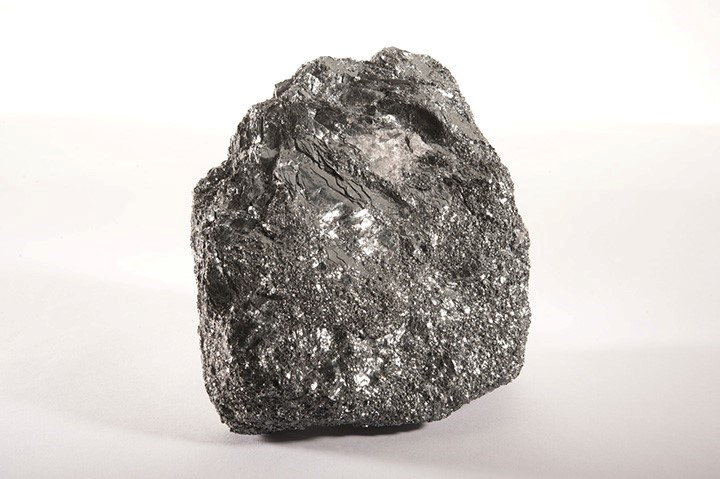
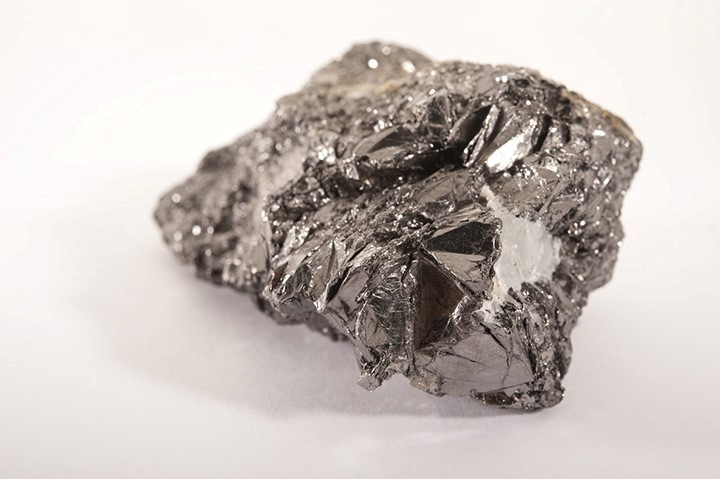
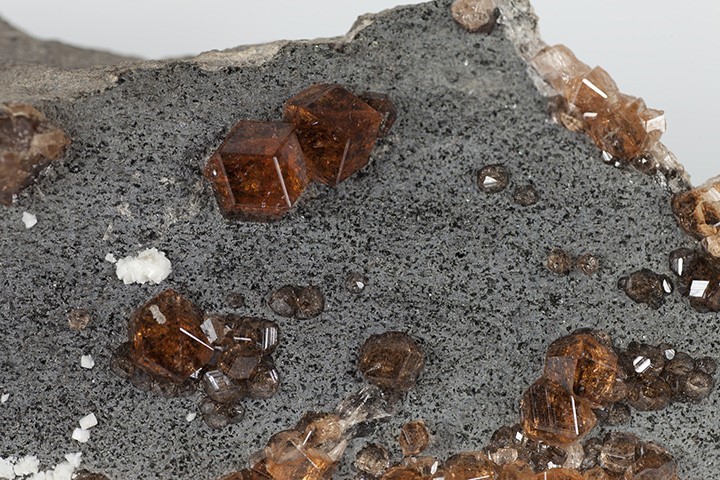
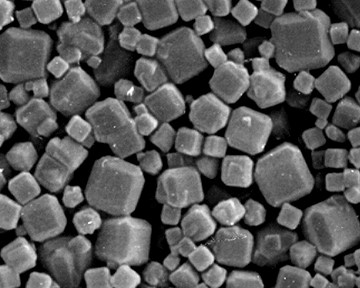
Arsenic (As)
Arsenic occurs in its native state or, more commonly, as iron, nickel or cobalt arsenides and sulfoarsenides. Arsenic is generally associated with antimony and precious metals such as gold and silver.

Chromium (Cr)
Chromium is a fairly abundant transition metal. Chromite is a commun accessory mineral in mafic and ultramafic igneous rocks. Locally, elevated concentrations of chromite (chromitite) can be observed in these rocks and in their altered or metamorphosed conterparts (dunite, peridotie, serpentinite).

Platinum Group Elements (PGEs)
Platinum Group Elements (PGEs) include elements related to platinum (Pt) including palladium (Pd), rhodium (Rh), ruthenium (Ru), iridium (Ir) and osmium (Os). They are generally associated with magmatic copper-nickel or chromium mineralization.
Platinum (Pt) Palladium (Pd) Rhodium (Rh) Ruthenium (Ru) Iridium (Ir) Osmium (Os)
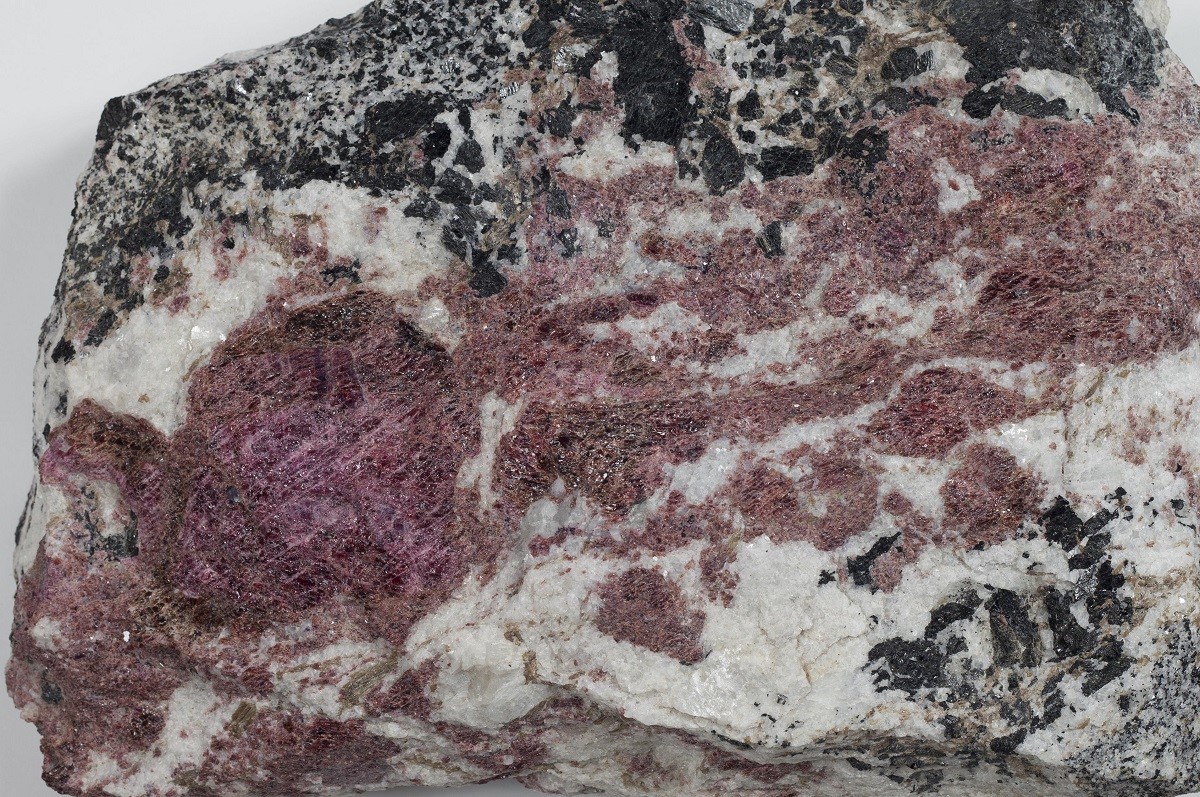
Rare earth elements (REEs)
Rare earth elements are a group of metals comprising the fifteen lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium. In elemental form, REEs have a metallic appearance and are fairly soft, malleable and ductile. Mineralization is associated with intrusive magmatic rocks (carbonatite, alkaline or hyperalkaline rocks), metasomatic rocks or placer deposits.
Cerium (Ce) Lanthanum (La) Neodymium (Nd) Praseodymium (Pr)Samarium (Sm) Europium Ytterbium

Indium (In)
Indium is co-produced by the metallurgy associated with zinc.