Glacial Erosional Forms
The theme of glacial erosion forms includes microforms and landforms produced by glacial erosion (e.g. striations, grooves, boulders, etc.). The recognition of these marks, their distribution and the observation of polarity criteria allow the interpretation of the direction and sense of ice flow and the reconstruction of the evolution of glacial transport for a given territory. Glacial erosion marks are represented on maps of surficial deposits as a dot and are superimposed on morphosedimentological zones.
The list of symbols is also available in PDF format.
-
 ASCPoint
ASCPoint -
 ASIPoint
ASIPoint -
 BCNPoint
BCNPoint -
 BCVPoint
BCVPoint -
 BCHPoint
BCHPoint -
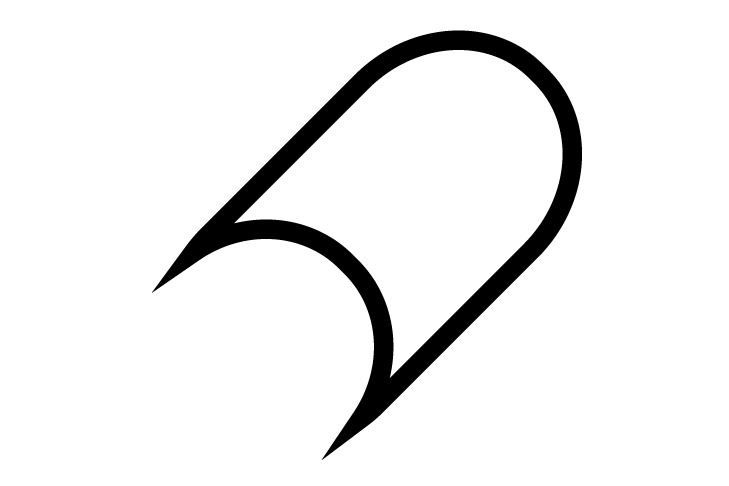 CSCPoint
CSCPoint -
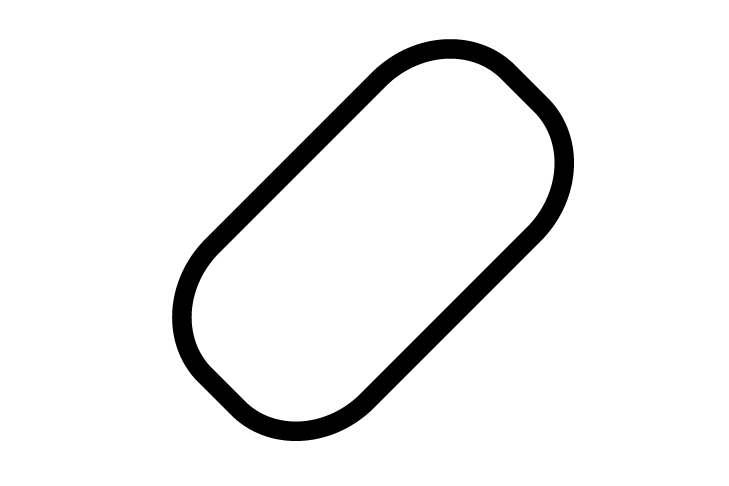 CSIPoint
CSIPoint -
 CABPoint
CABPoint -
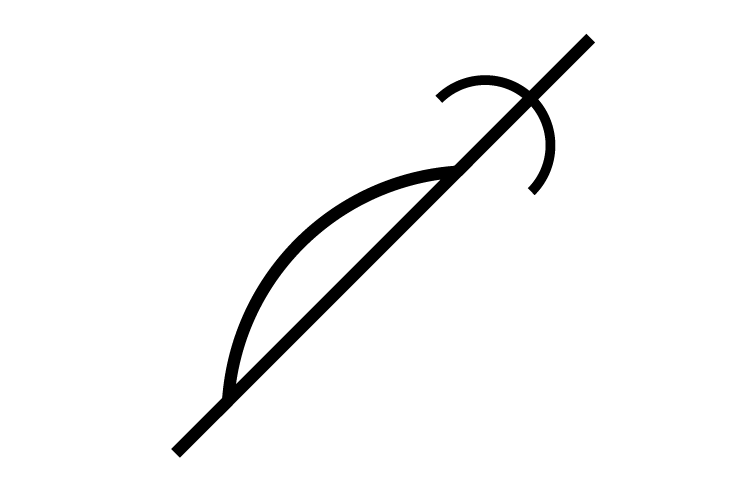 DOBPoint
DOBPoint -
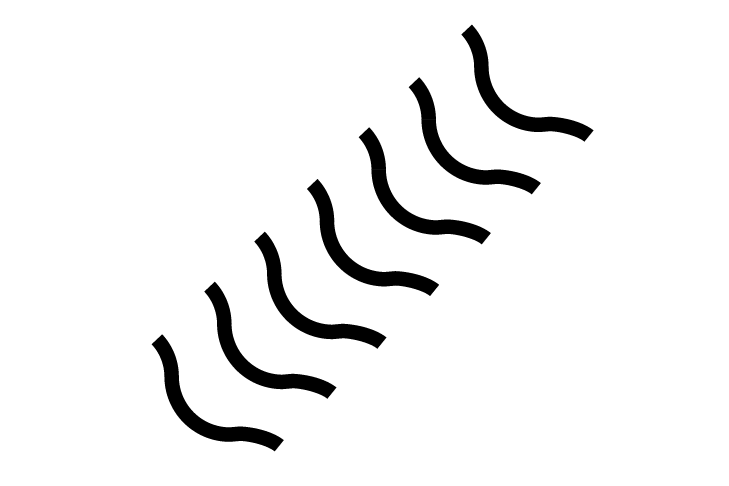 FRBPoint
FRBPoint -
 FSCPoint
FSCPoint -
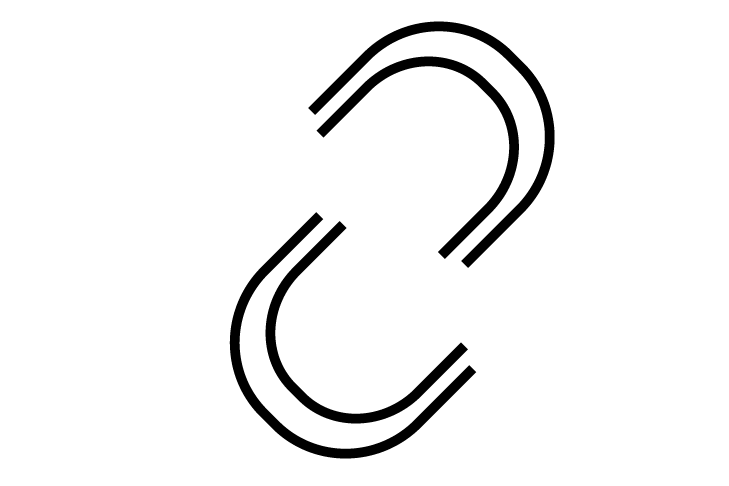 FSIPoint
FSIPoint -
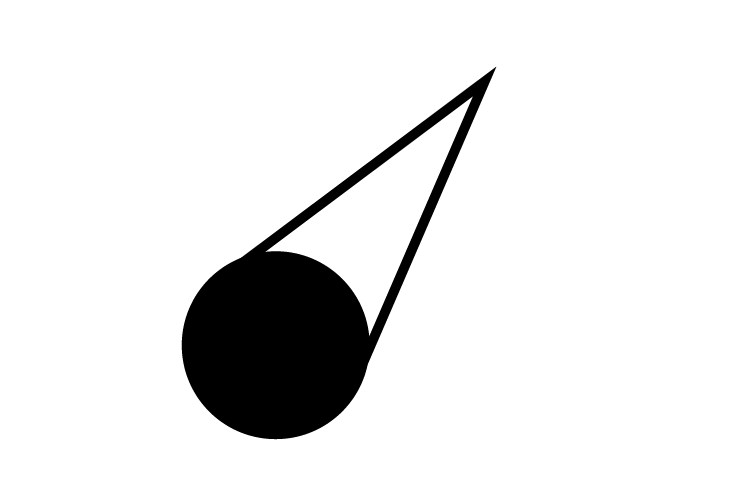 QDRPoint
QDRPoint -
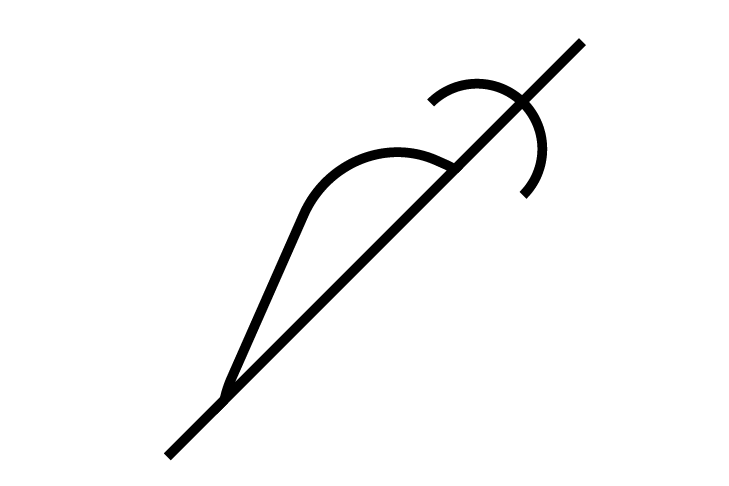 ROMPoint
ROMPoint -
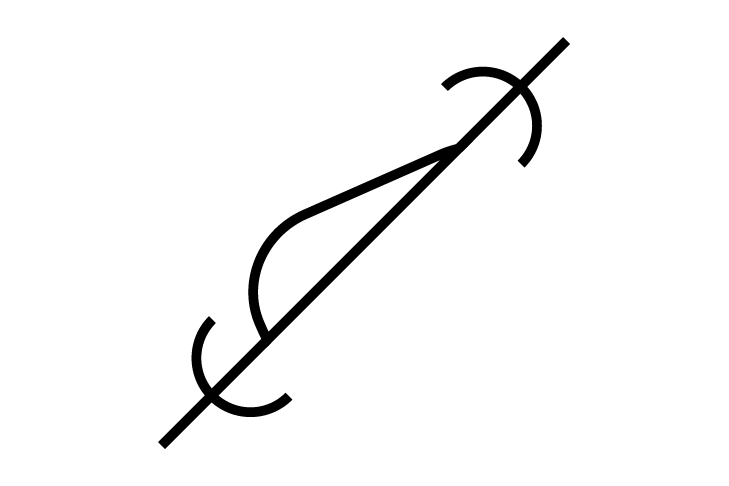 ROPPoint
ROPPoint -
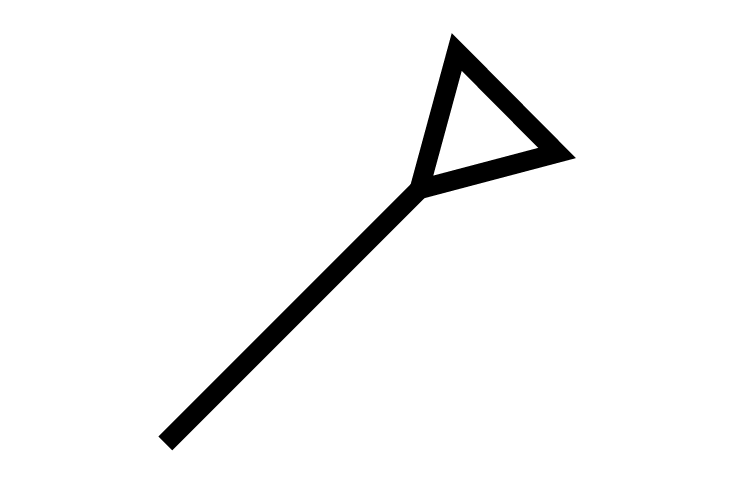 STCPoint
STCPoint -
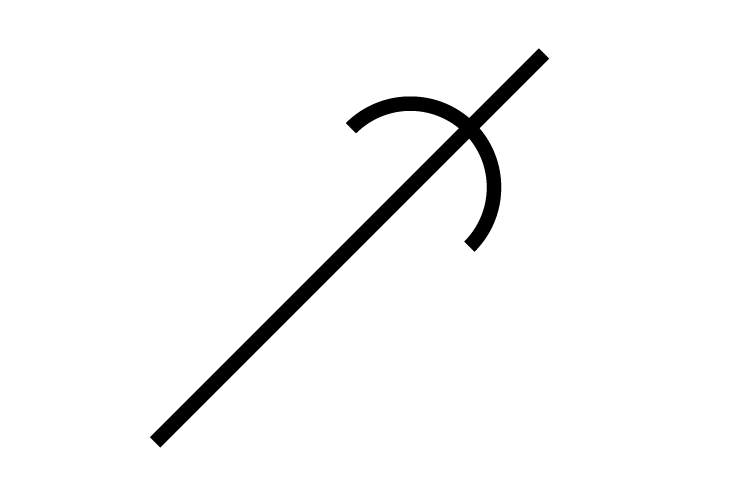 STSCPoint
STSCPoint -
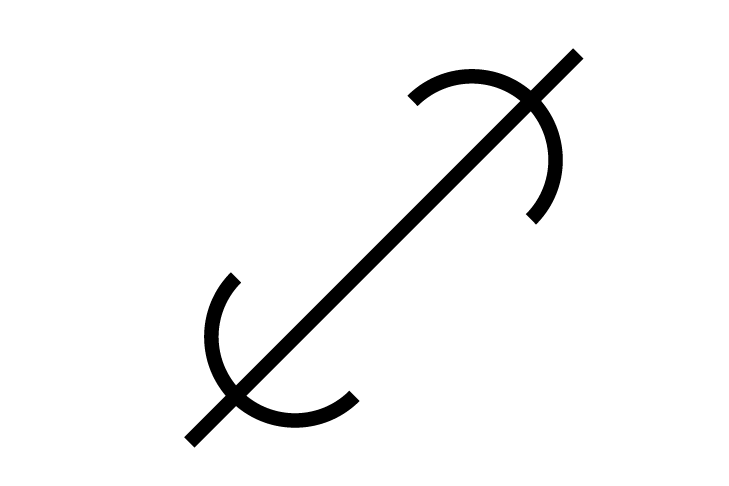 STSIPoint
STSIPoint
